ipstack
LAST UPDATED: APR 11, 2025
Overview
ipstack retrieves geolocation information about IP addresses.
D3 SOAR is providing REST operations to function with ipstack.
READER NOTE
ipstack serves as D3 SOAR's data source for obtaining geolocation details for artifacts displayed in the Map View of the Monitor module. For more information, refer to the FAQ section.
ipstack is available for use in:
Known Limitations
The maximum number of monthly requests to ipstack's API is dependent on your ipstack account's subscription plan. Please refer to https://ipstack.com/product for more information about pricing plans and request limits.
Connection
To connect to ipstack from D3 SOAR, please follow this part to collect the required information below:
Parameter | Description | Example |
Server URL | The server URL of the ipstack API. | http://api.ipstack.com |
Access Key | The access key to authenticate the API connection. | 2c66d419c0g2b70d8c18d8388e30ed22 |
READER NOTE
The prerequisite for using this guide is an ipstack account. To create a new account, navigate to Sign Up: ipstack to get started.
Configuring ipstack to Work with D3 SOAR
Log in to your ipstack account at https://ipstack.com/login. If you do not have an account, navigate to Sign Up: ipstack to create a new one.
READER NOTE
The free account's API allows you to run the Query IP command, but has a limitation on the number of requests.
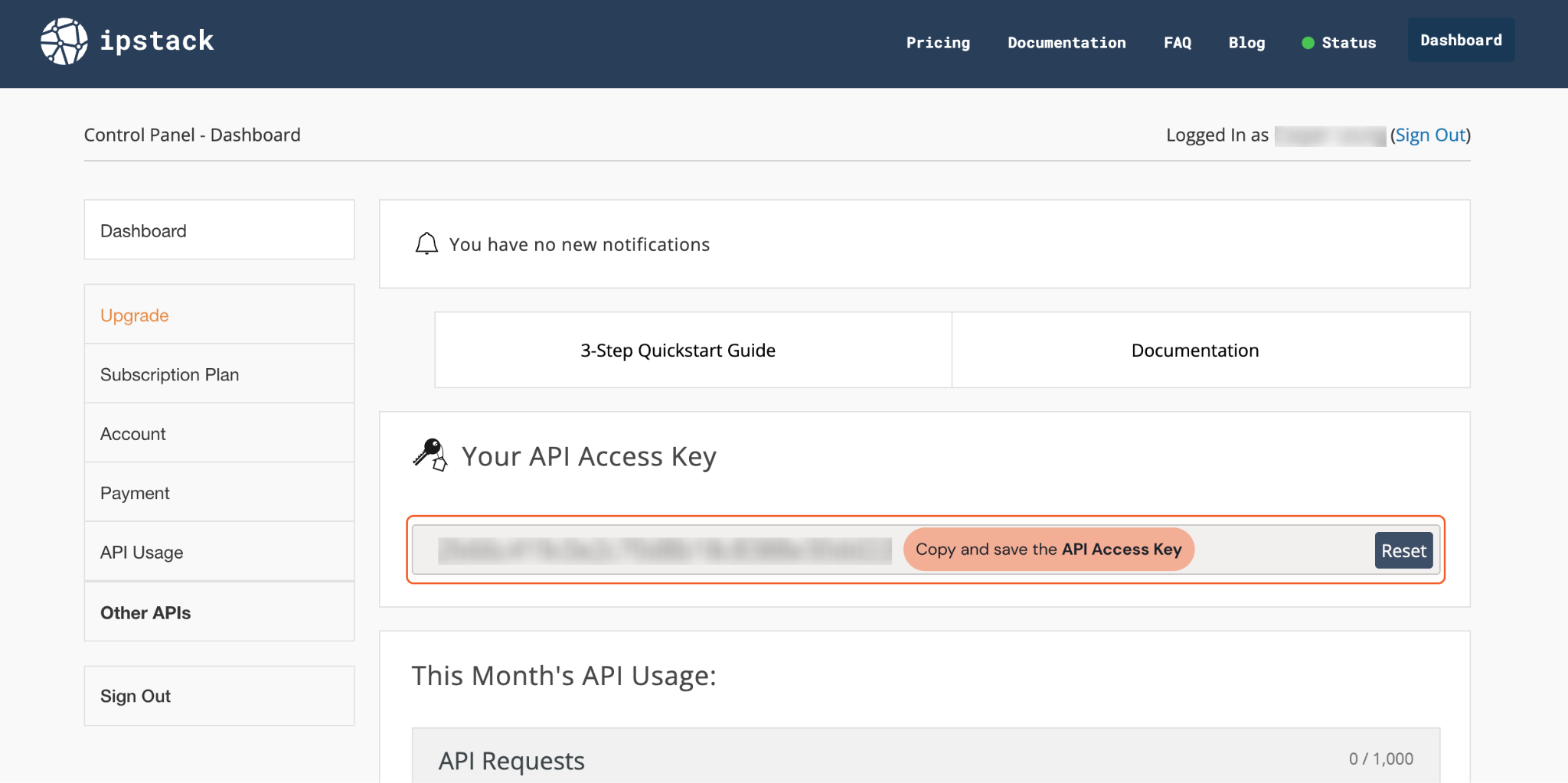
Once logged in you will see your API Access Key. Copy and store it in a secure location. It will be required to build an integration connection in D3 SOAR.
Configuring D3 SOAR to Work with ipstack
Log in to D3 SOAR.
Find the ipstack integration.
.png?inst-v=6361910a-bb09-40c1-b002-132967d8f223)
Navigate to Configuration on the top header menu.
Click on the Integration icon on the left sidebar.
Type ipstack in the search box to find the integration, then click it to select it.
Click + Connection, on the right side of the Connections section. A new connection window will appear.
Configure the following fields to create a connection to ipstack.
.png?inst-v=6361910a-bb09-40c1-b002-132967d8f223)
Connection Name: The desired name for the connection.
Site: Specifies the site to use the integration connection. Use the drop-down menu to select the site. The Share to Internal Sites option enables all sites defined as internal sites to use the connection. Selecting a specific site will only enable that site to use the connection.
Note: When configuring a connection for the map view feature in Monitor, your selection determines which D3 SOAR sites can utilize this connection for retrieving and mapping geolocations of artifacts.Recipient site for events from connections Shared to Internal Sites: This field appears if you selected Share to Internal Sites for Site to let you select the internal site to deploy the integration connection.
Agent Name (Optional): Specifies the proxy agent required to build the connection. Use the dropdown menu to select the proxy agent from a list of previously configured proxy agents.
Description (Optional): Add your desired description for the connection.
Tenant (Optional): When configuring the connection from a master tenant site, you have the option to choose the specific tenant sites you want to share the connection with. Once you enable this setting, you can filter and select the desired tenant sites from the dropdowns to share the connection.

Configure User Permissions: Defines which users have access to the connection.
Active: Check the tick box to ensure the connection is available for use.
.png?inst-v=6361910a-bb09-40c1-b002-132967d8f223)
System: This section contains the parameters defined specifically for the integration. These parameters must be configured to create the integration connection.
1. Input the Server URL. The default value is http://api.ipstack.com.
2. Input the saved Access Key from ipstack. Refer to step 2 of Configuring ipstack to Work with D3 SOAR.Enable Password Vault: An optional feature that allows users to take the stored credentials from their own password vault. Please refer to the password vault connection guide if needed.
Test the connection.
.png?inst-v=6361910a-bb09-40c1-b002-132967d8f223)
Click Test Connection to verify the account credentials and network connection. If the Test Connection Passed alert window appears, the test connection is successful. You will see Passed with a green checkmark appear beside the Test Connection button. If the test connection fails, please check your connection parameters and try again.
Click OK to close the alert window.
Click + Add to create and add the configured connection.
Commands
ipstack includes the following executable commands for users to set up schedules or create playbook workflows. With the Test Command, you can execute these commands independently for playbook troubleshooting.
Integration API Note
For more information about the ipstack API, please refer to the ipstack API reference.
Query IP
Retrieves geolocation information of the given IP addresses.
Input
Input Parameter | Required /Optional | Description | Example |
IPs | Required | The IPv4 or IPv6 addresses to retrieve geolocation information. You can also enter domain URLs to have ipstack resolve the domains to the underlying IP addresses. Note: The maximum number of allowed values is 50. | [ "8.8.8.8", "8.8.8.9" ] |
Output
Error Handling
If the Return Data is Partially Successful or Failed, an Error tab will appear in the Test Result window.
The error tab contains the details responded from D3 SOAR or third-party API calls, including Failure Indicator, Status Code, and Message. This can help you locate the root cause of a command failure.
Parts in Error | Description | Example |
Failure Indicator | Indicates the command failure that happened at a specific input and/or API call. | Query IP failed. |
Status Code | The response code issued by the third-party API server or the D3 SOAR system that can be used to locate the corresponding error category. For example, if the returned status code is 401, the selected connection is unauthorized to run the command. The user or system support would need to check the permission setting in the ipstack portal. Refer to the HTTP Status Code Registry for details. | Status Code: 401. |
Message | The raw data or captured key error message from the integration API server about the API request failure. | Message: The IP Address supplied is invalid. |
Error Sample Data Query IP failed. Status Code: 401. Message: The IP Address supplied is invalid. |
FAQ
Question 1: How is ipstack used for the map view in Monitor?
ipstack is used as the data source to retrieve geolocation information of artifacts with the built-in External Endpoint artifact type, which are then displayed on the map view. The following conditions must be met in order to have IP and host domains displayed in map view.
The required setup includes:
ipstack Integration: A connection to the ipstack integration must be established on the target site.
Field Mappings: Ensure the field mappings of your data sources' Fetch Event commands are correctly set. The IP addresses in the data sources' raw data need to be linked to the External Endpoint artifact type.
Within the field mapping settings of your data sources, map the JSON path of these IP addresses to any one of the following default fields: Destination hostname, Destination IP address, Source hostname, Source IP address, Device, Device IP address, Source Device, Source Device IP address, Destination Device and Destination Device IP address. This will link the associated IPs with the External Endpoint artifact type.
Alerts with IP or host domain information are ingested into D3 SOAR as events.
With the corresponding field mappings in place, the system automatically checks the IP geolocation in ipstack upon ingesting events from the configured data sources.
READER NOTE
D3 SOAR will first perform an IP geolocation check in the system's cache. If no data is found, it will proceed to check in ipstack, using up the allocated quota.
If ipstack returns an IP geolocation, it will be displayed on the map view.
READER NOTE
If ipstack doesn't return any result, the IP or host domain won't be displayed on the map view.