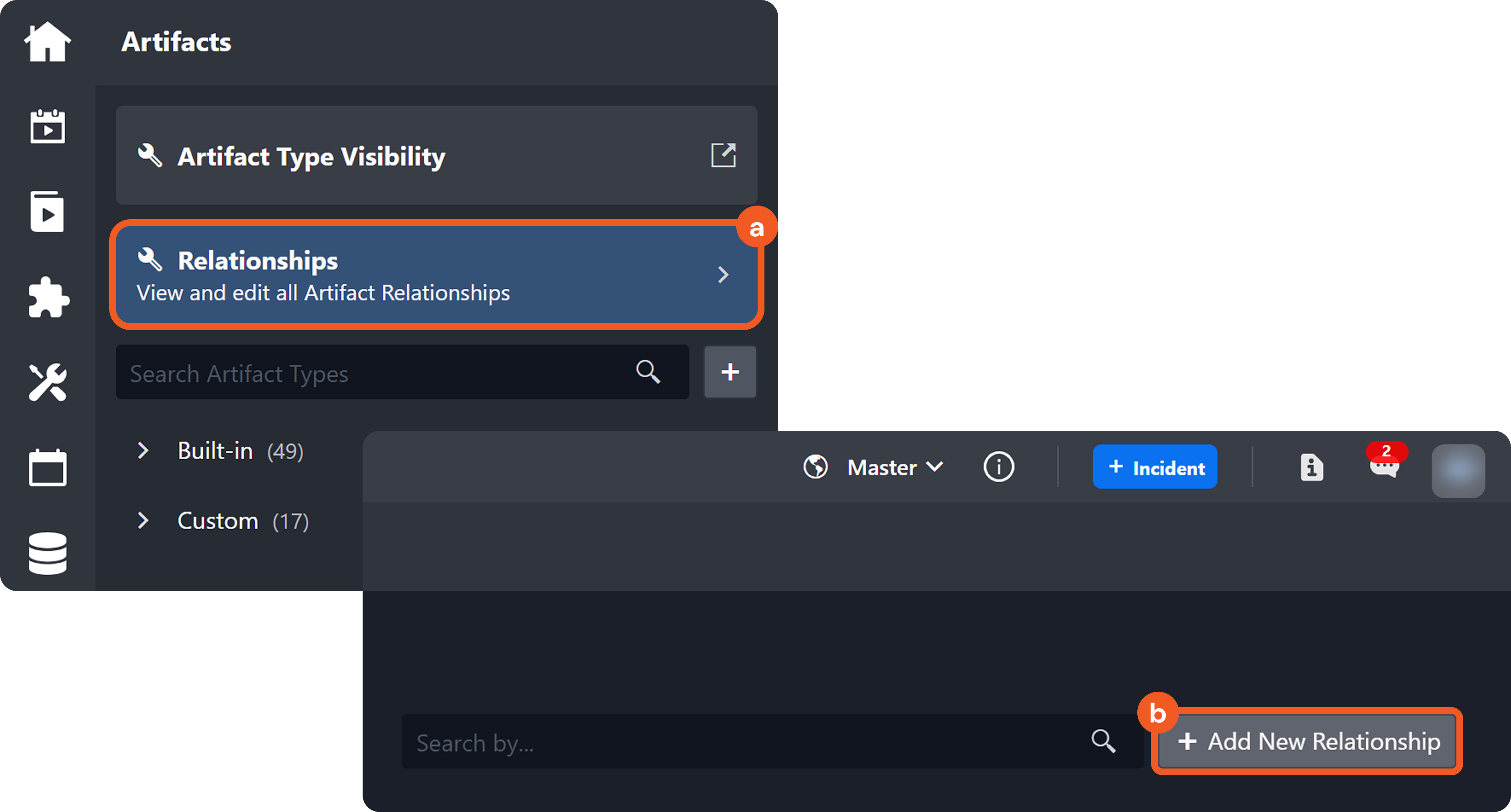
Artifact Relationships
LAST UPDATED: SEPTEMBER 19, 2025
PREREQUISITES
Knowledge of field mapping.
Knowledge of artifact instantiation.
Artifact relationships define how different artifact entities interact and influence one another. By configuring relationships, analysts can model real-world behaviors, visualize connections on the Artifact Behavior diagram, and understand how multiple entities link together.
Worked Examples
PART 1 Relationship Configuration and Insights
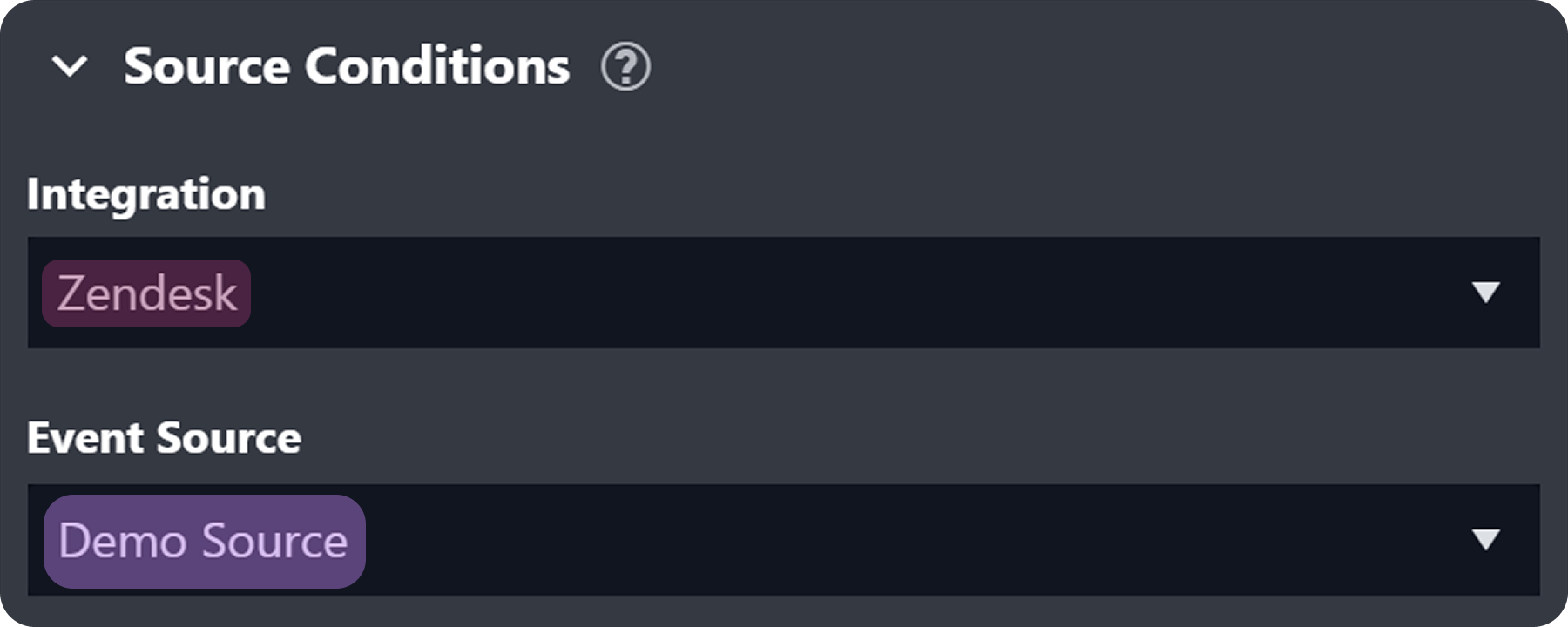
Set up the following event source.
%201-20250918-003055.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
Add the following two EFM records:
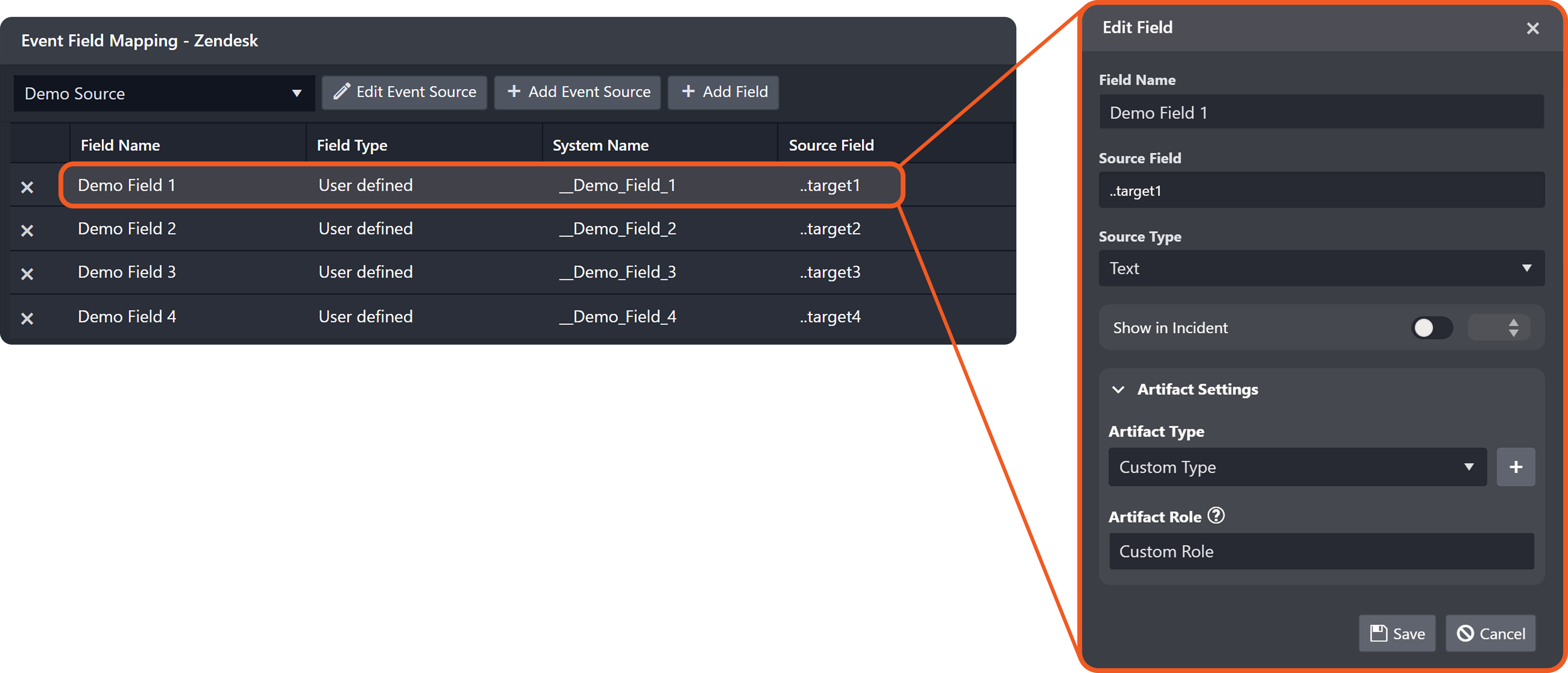
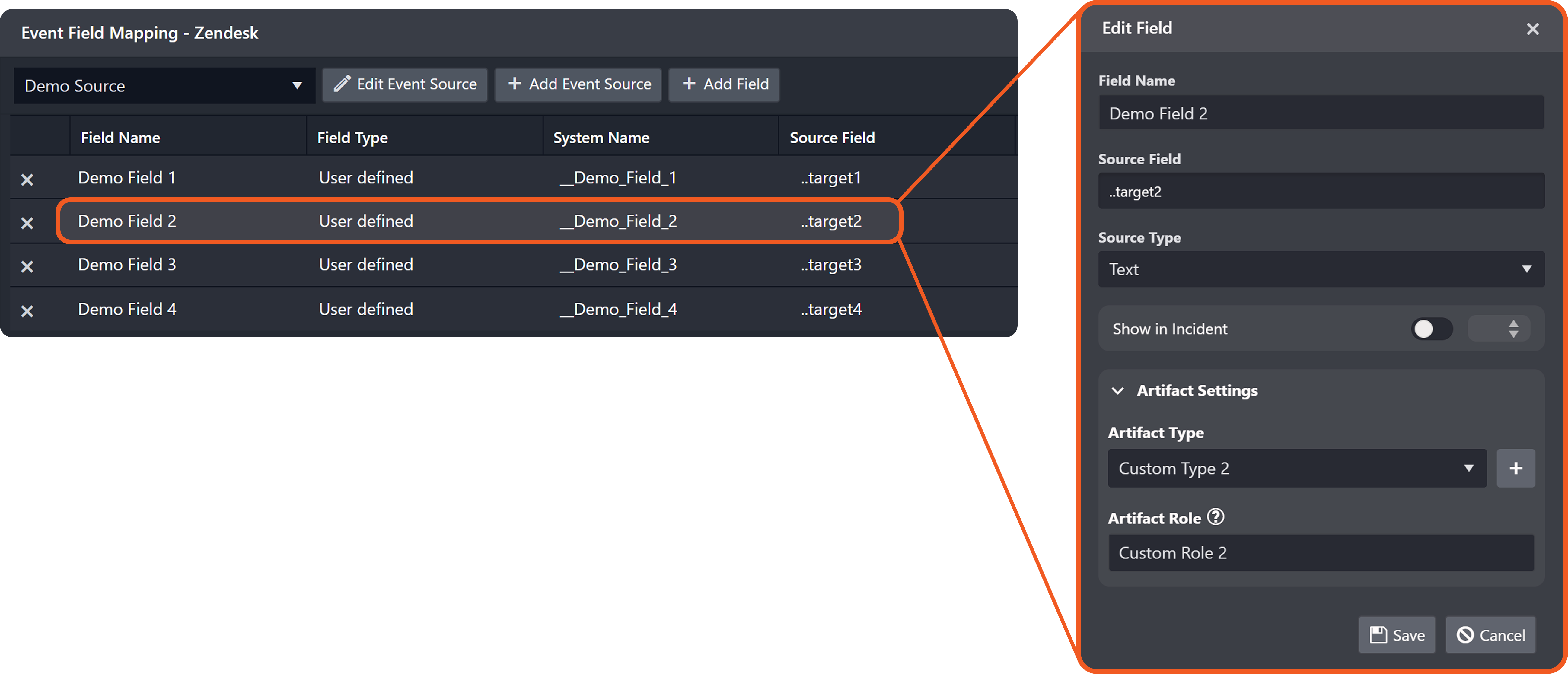
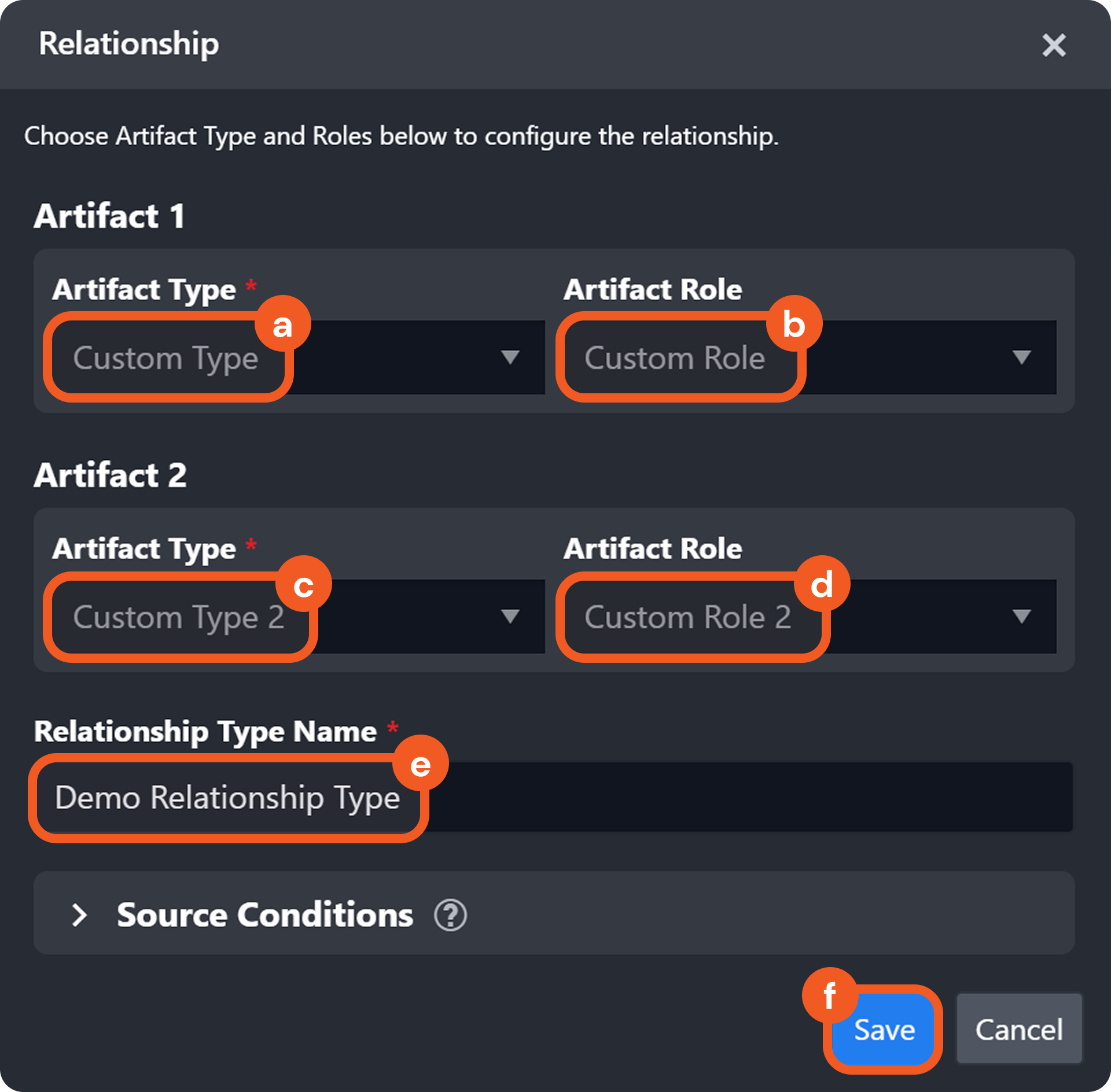
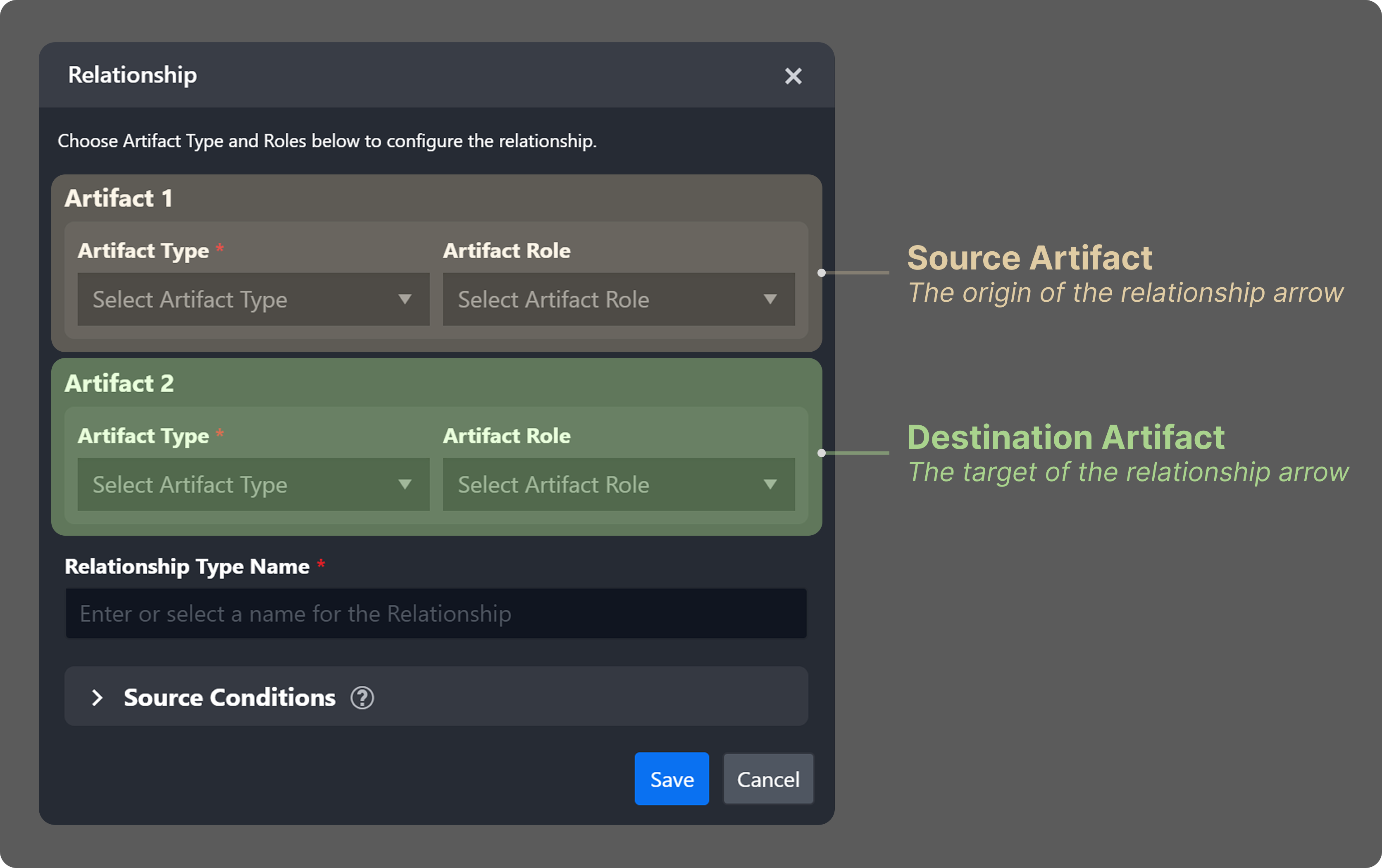
Add the following relationship.
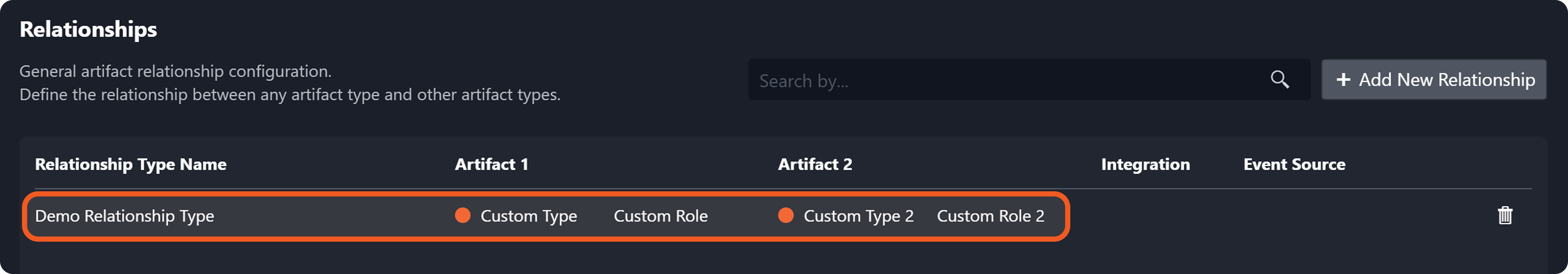
Verify that a corresponding relationship record has been added to the table.
Send the following POST webhook request.
JSON{ "results": [ { "id": "0008", "discriminator": "demo", "target1": "value1", "target2": "value2" } ] }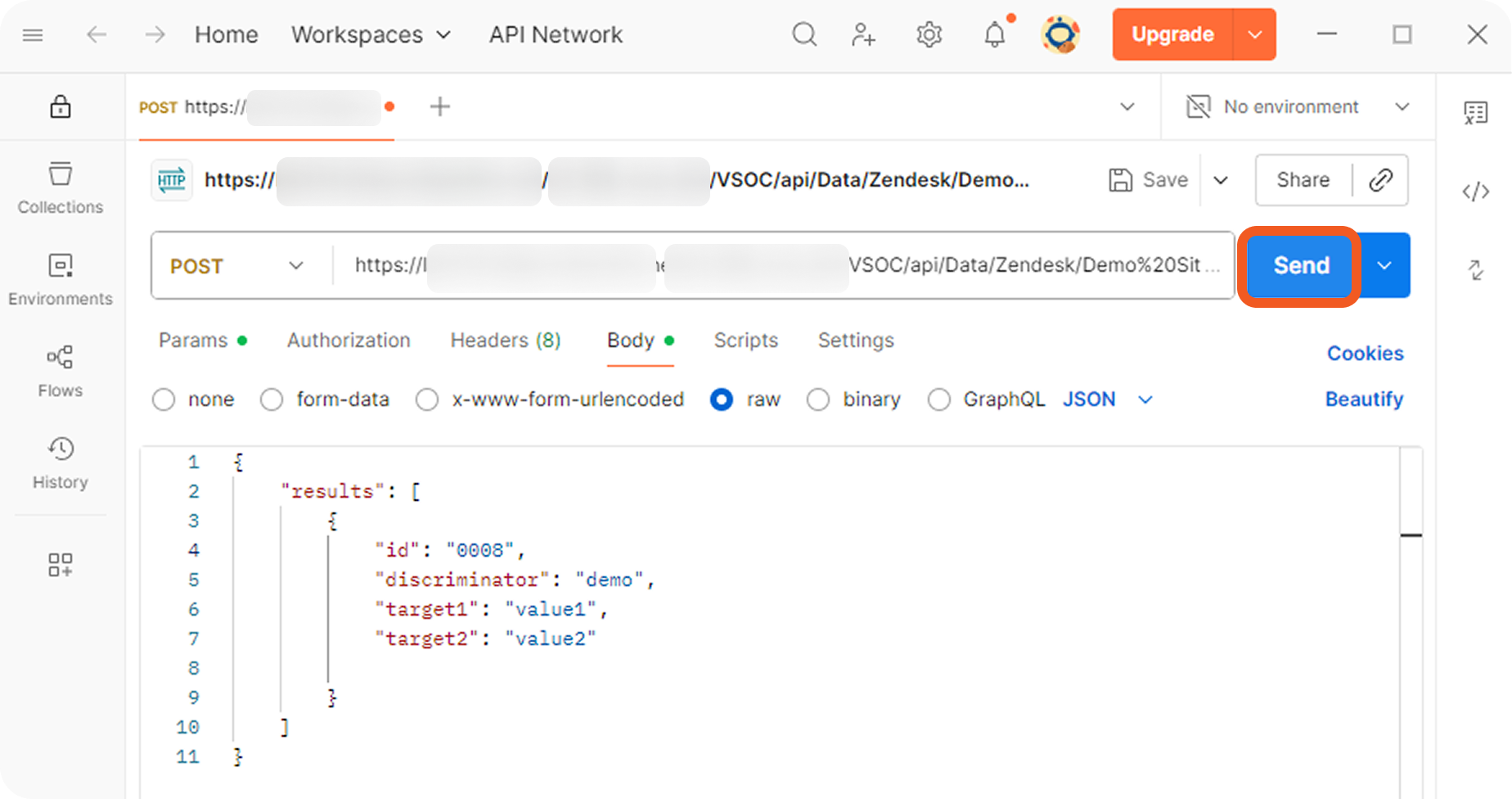
Verify that two artifact entities have been created and are linked by the configured relationship.
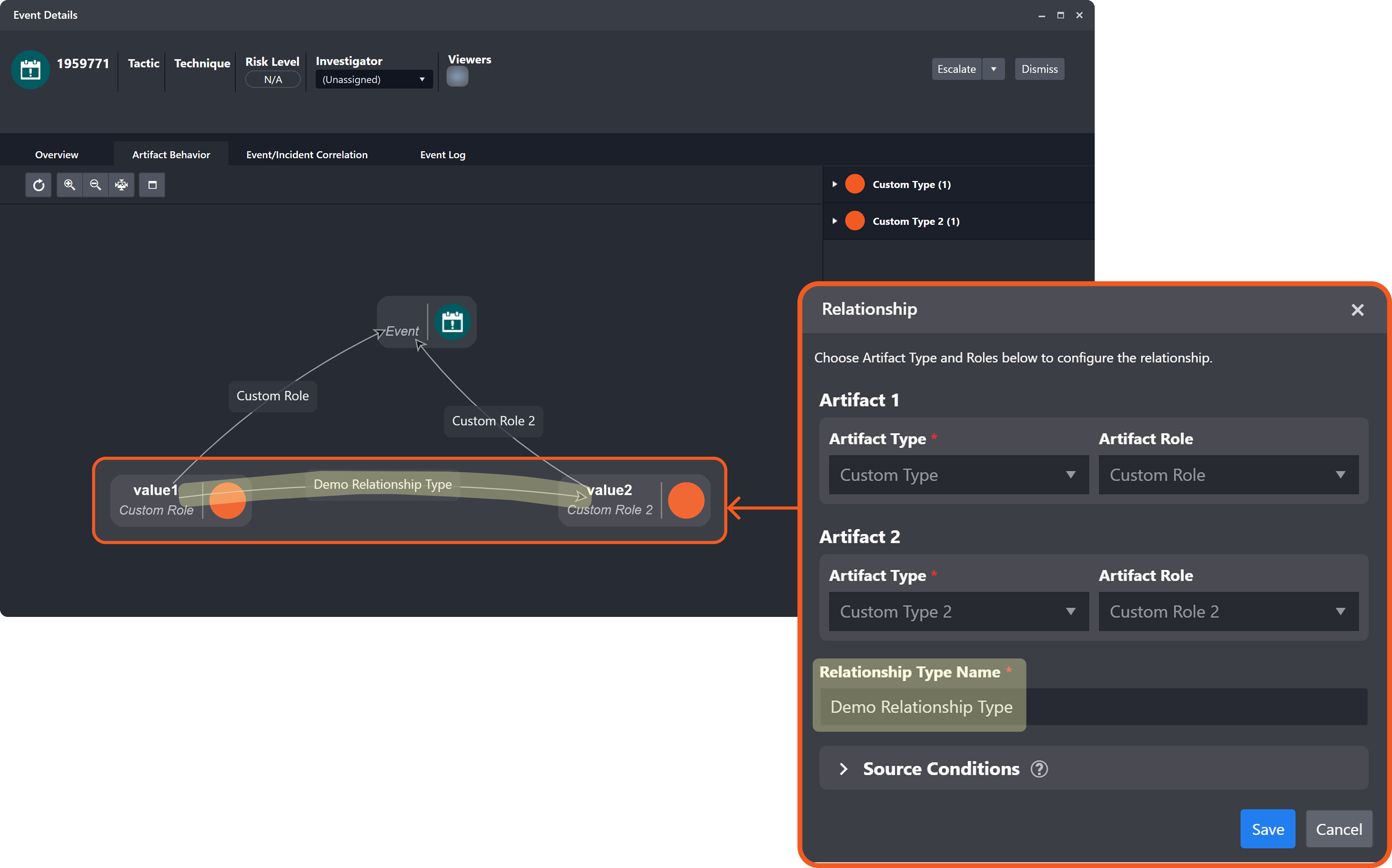
PART 2 Alternative Example with Additional Artifact Entities
Add the following two EFM records:
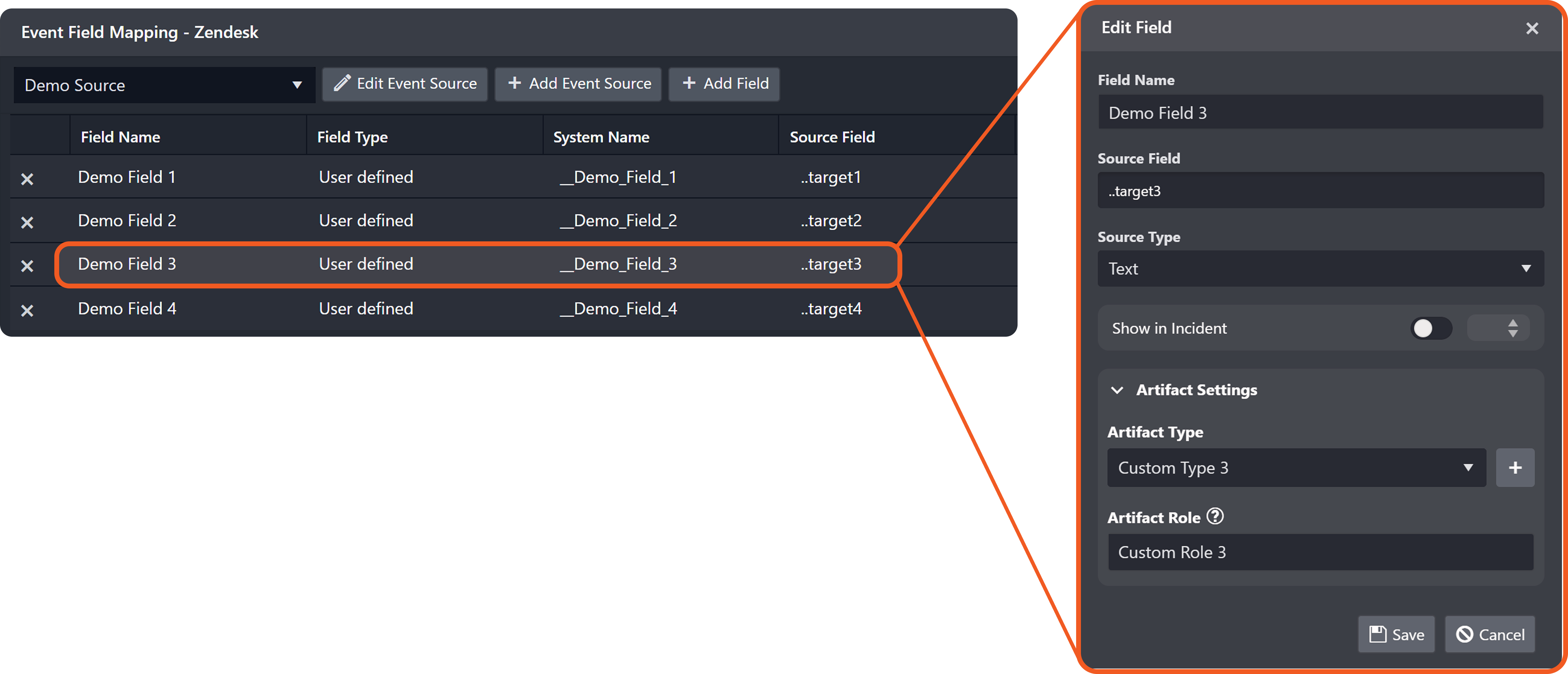
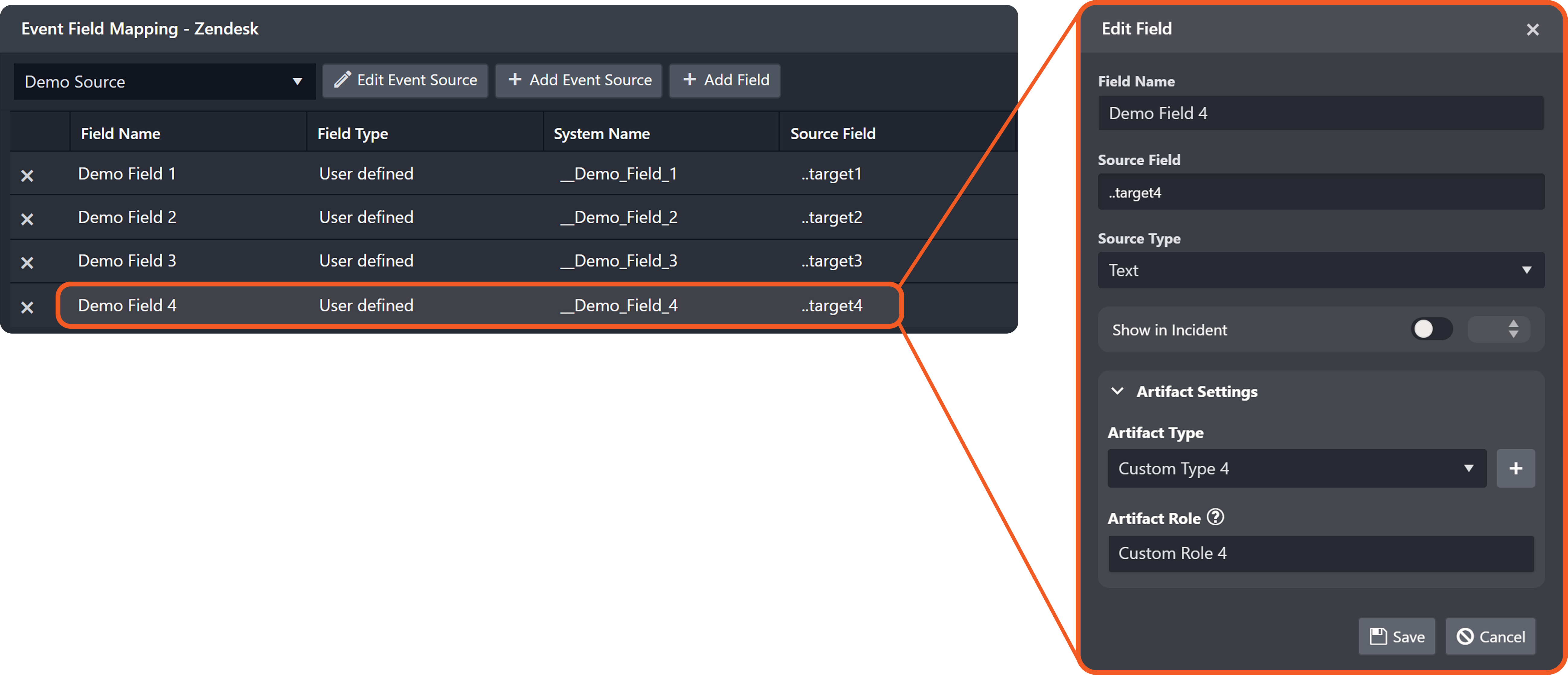
Delete the relationship configured in step 3.
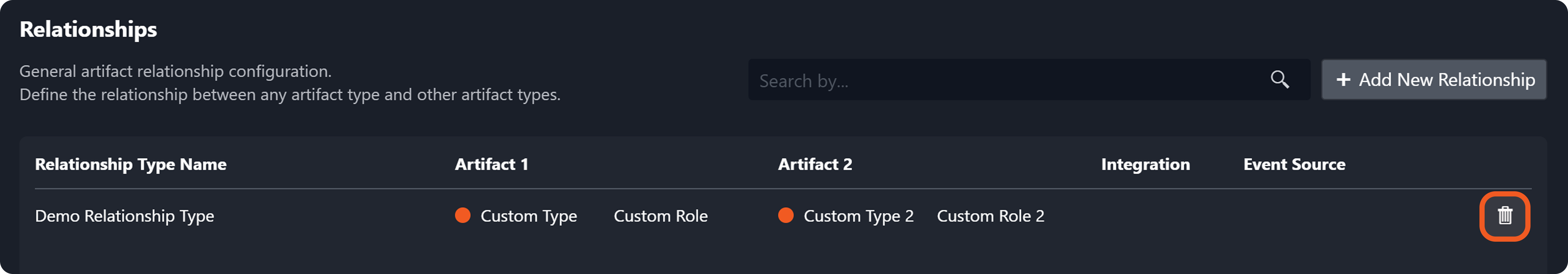
Add the following relationship.
-20250918-010935.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
Send the following POST webhook request.
JSON{ "results": [ { "id": "0010", "discriminator": "demo", "target1": "value1", "target2": "value2", "target3": "value3", "target4": "value4" } ] }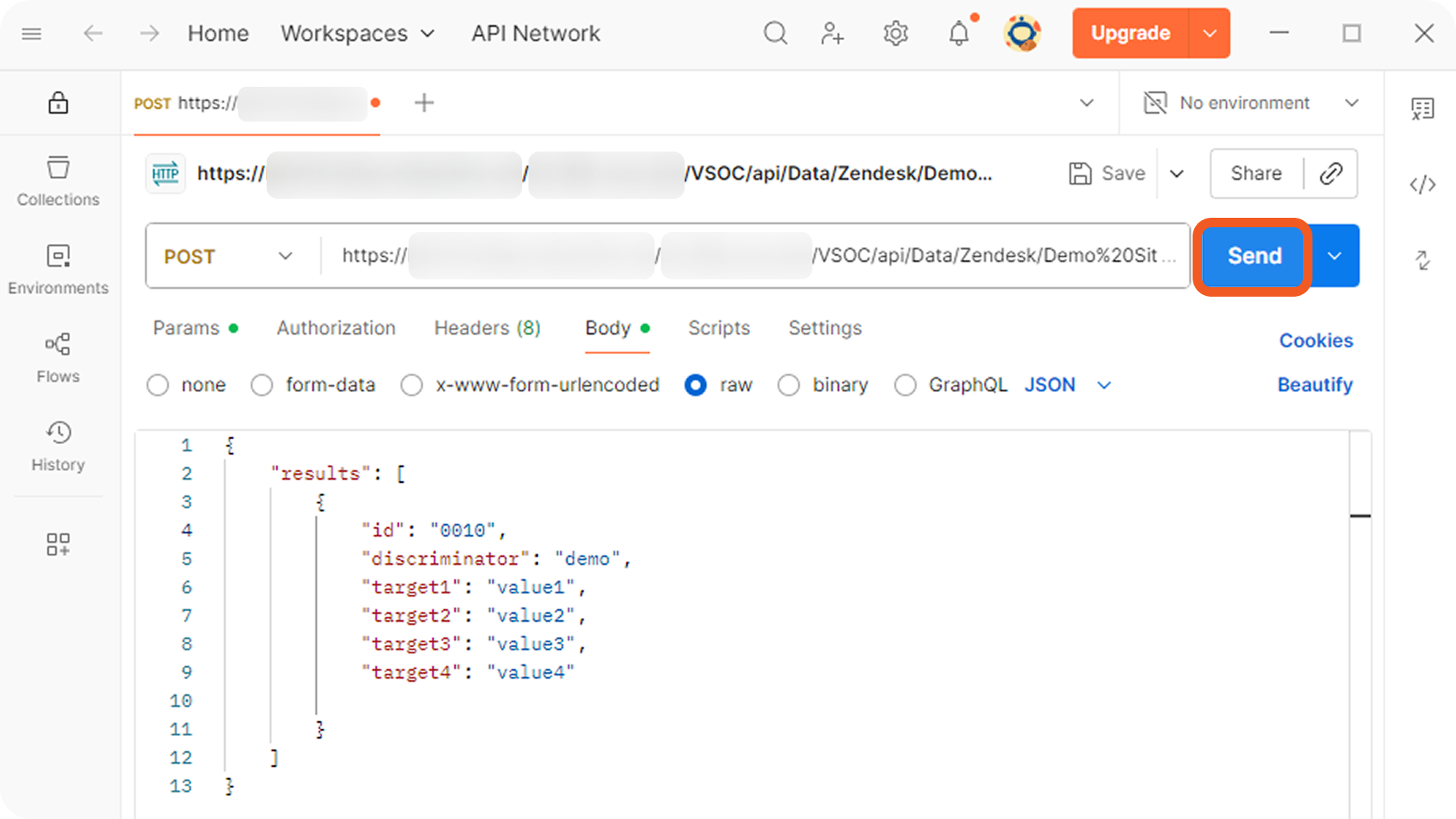
Verify that four artifact entities have been created, and that Custom Type 3 and Custom Type 4 are linked by the configured relationship.
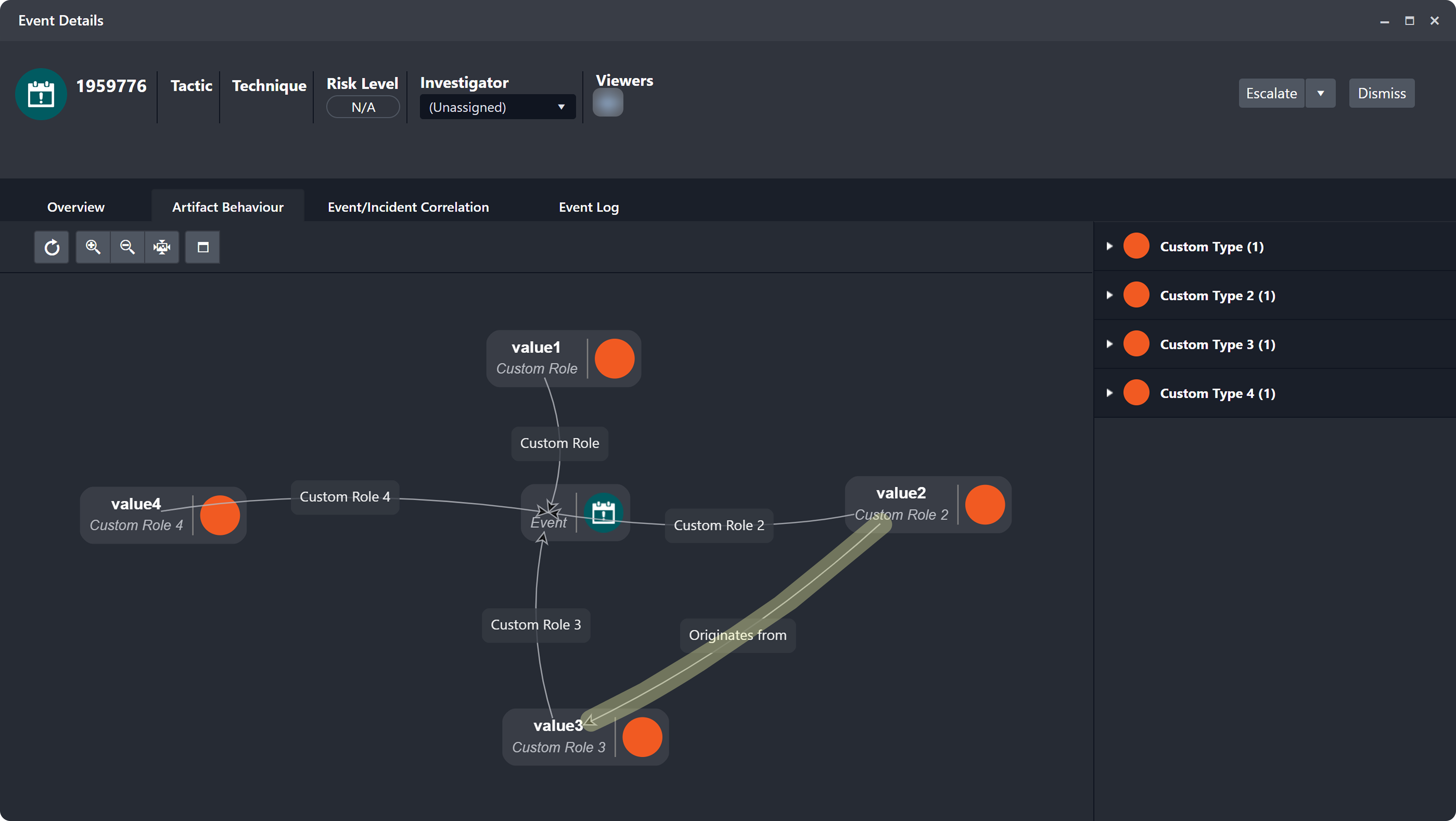
ROLE DISTINGUISHES ARTIFACT INSTANCES
When two EFM records are configured to instantiate the same artifact type but are assigned different roles, the resulting artifact instance whose role matches the one specified in the Relationship popover is used to form the relationship. See FAQ 1.
PART 3 Multiple Relationships
Add the following relationship.
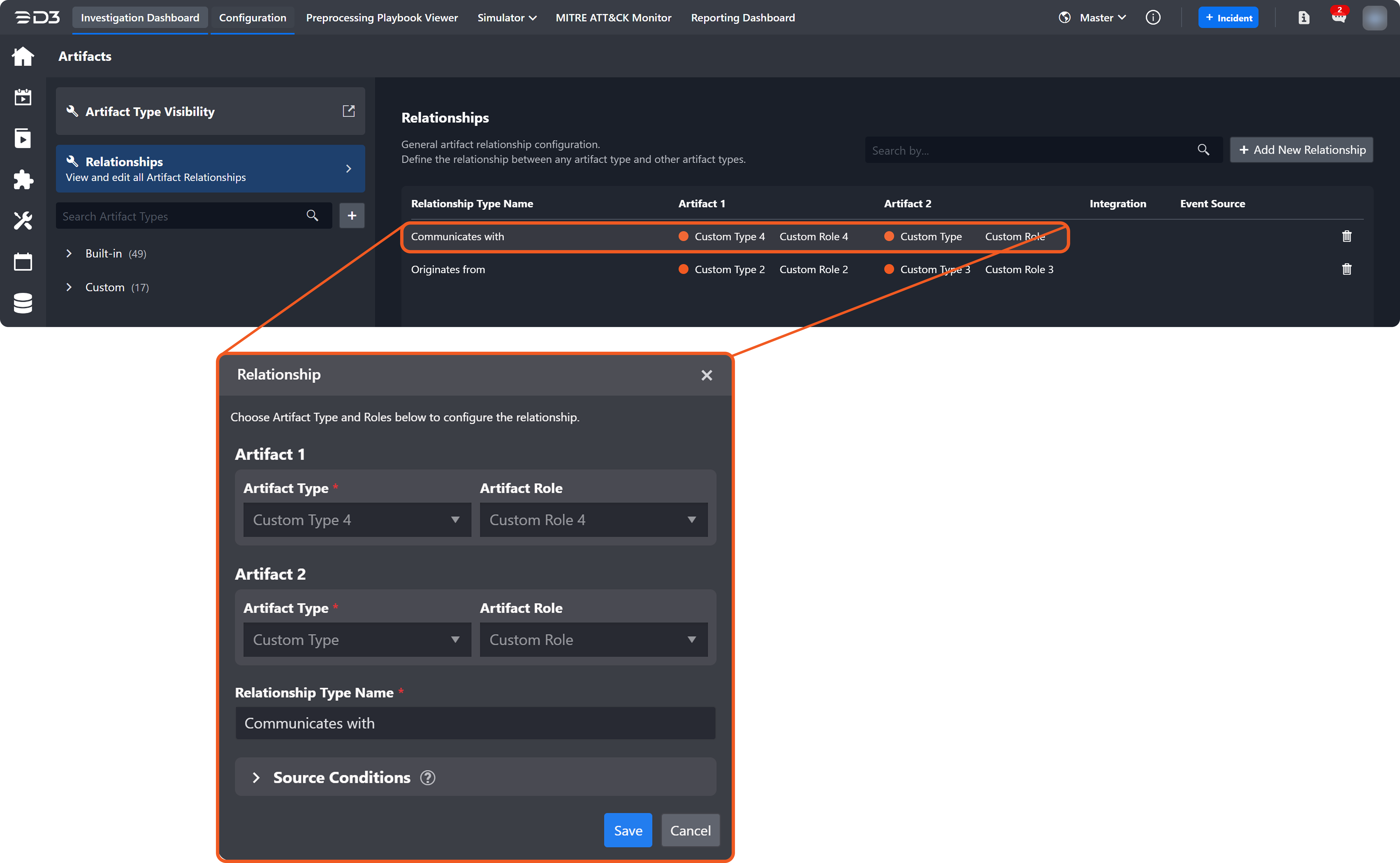
Send the following POST webhook request.
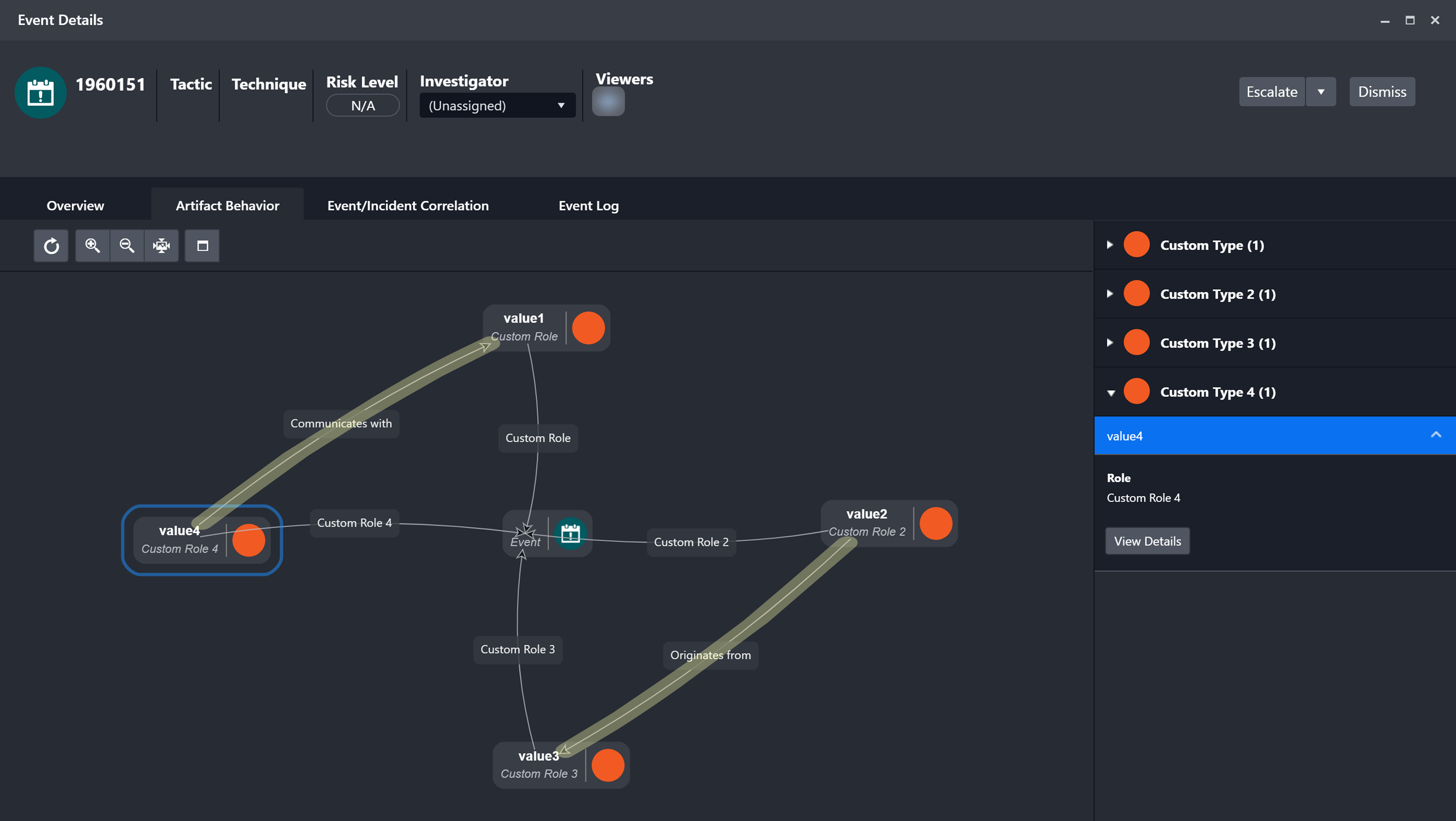
JSON{ "results": [ { "id": "0012", "discriminator": "demo", "target1": "value1", "target2": "value2", "target3": "value3", "target4": "value4" } ] }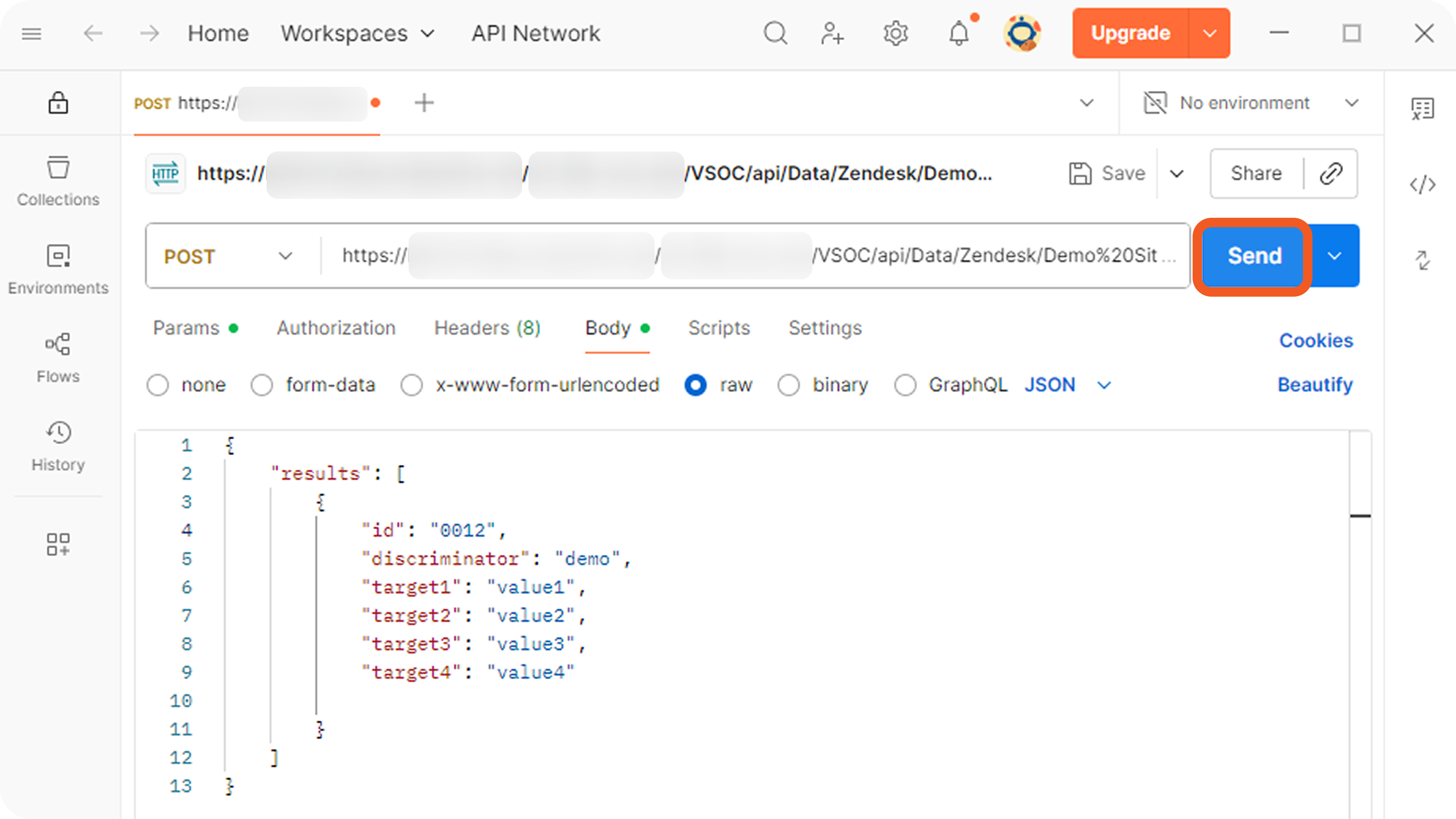
Verify in the new D3 event that adding the "Communicates with" relationship between the Custom Type artifact entity and the Custom Type 4 artifact entity results in two disconnected relationship groups.
PART 4 Modeling Complex Interactions
Add the following relationship.
-20250918-213101.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
Send the following POST webhook request.
JSON{ "results": [ { "id": "0014", "discriminator": "demo", "target1": "value1", "target2": "value2", "target3": "value3", "target4": "value4" } ] }-20250918-180231.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
Verify in the corresponding D3 event that adding the additional "Activates" relationship between the Custom Type 4 and Custom Type 3 artifact entities results in an interconnected, directed interaction flow.
-20250918-180915.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
%201-20250917-225614.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
%201-20250917-225626.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
%201-20250917-234712.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250918-211139.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250918-203911.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250918-205500.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250918-210418.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)