Artifact Instantiations
LAST UPDATED: SEPTEMBER 19, 2025
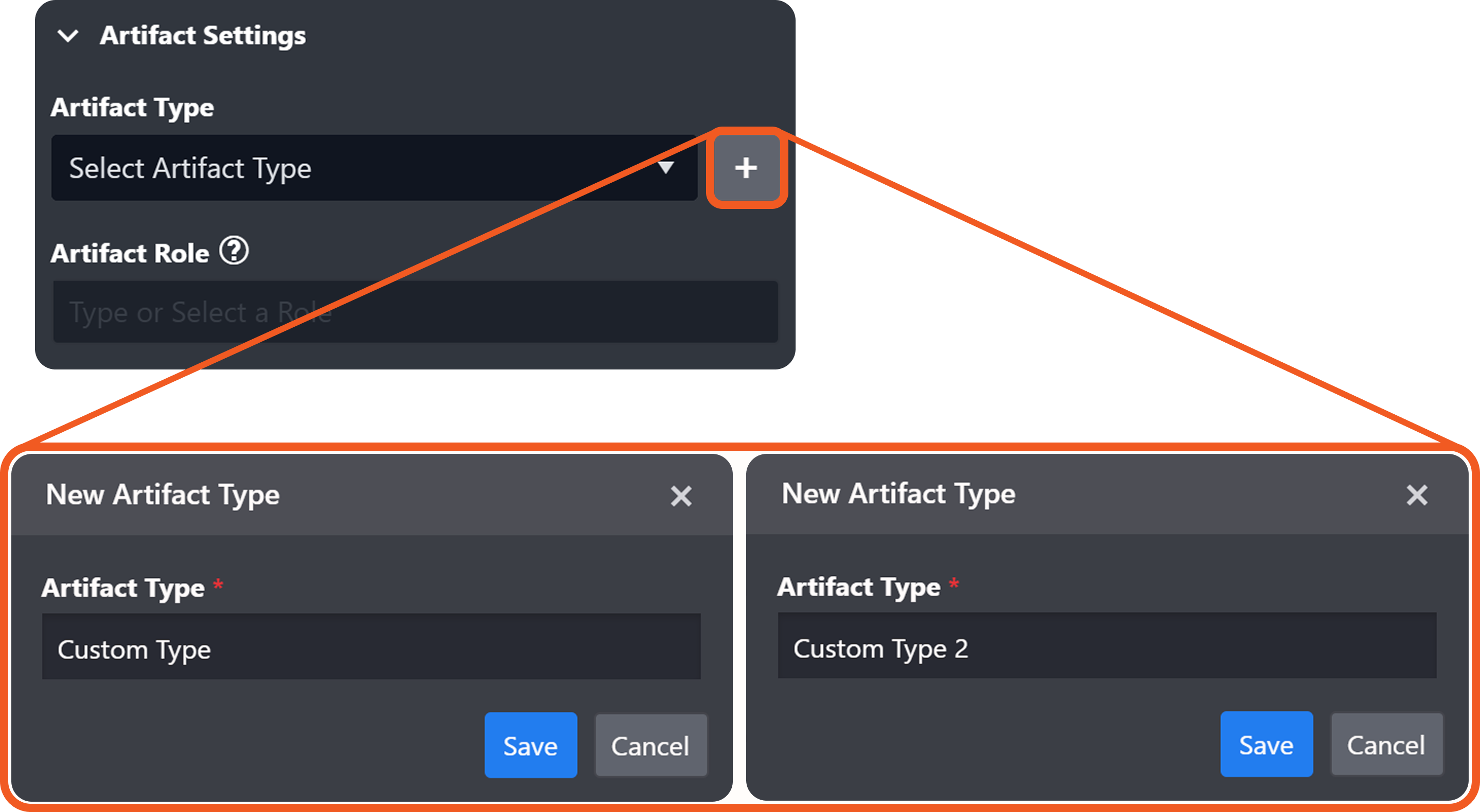
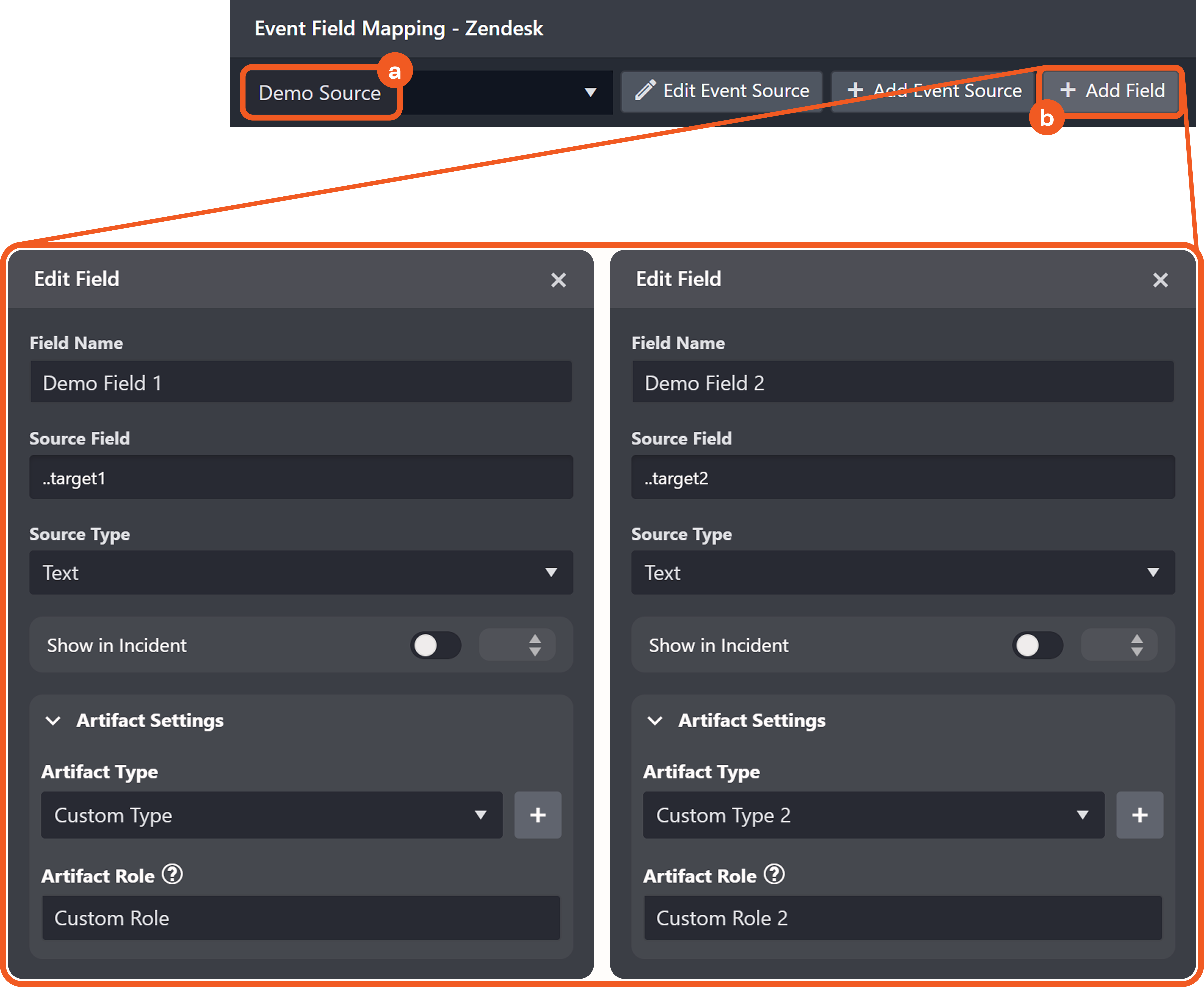
The optional Artifact Settings section in the EFM Edit Field popover defines the basis for instantiating an artifact type from ingested data. Artifact instantiations underpin relationship modeling and drive subsequent behavioral analysis.
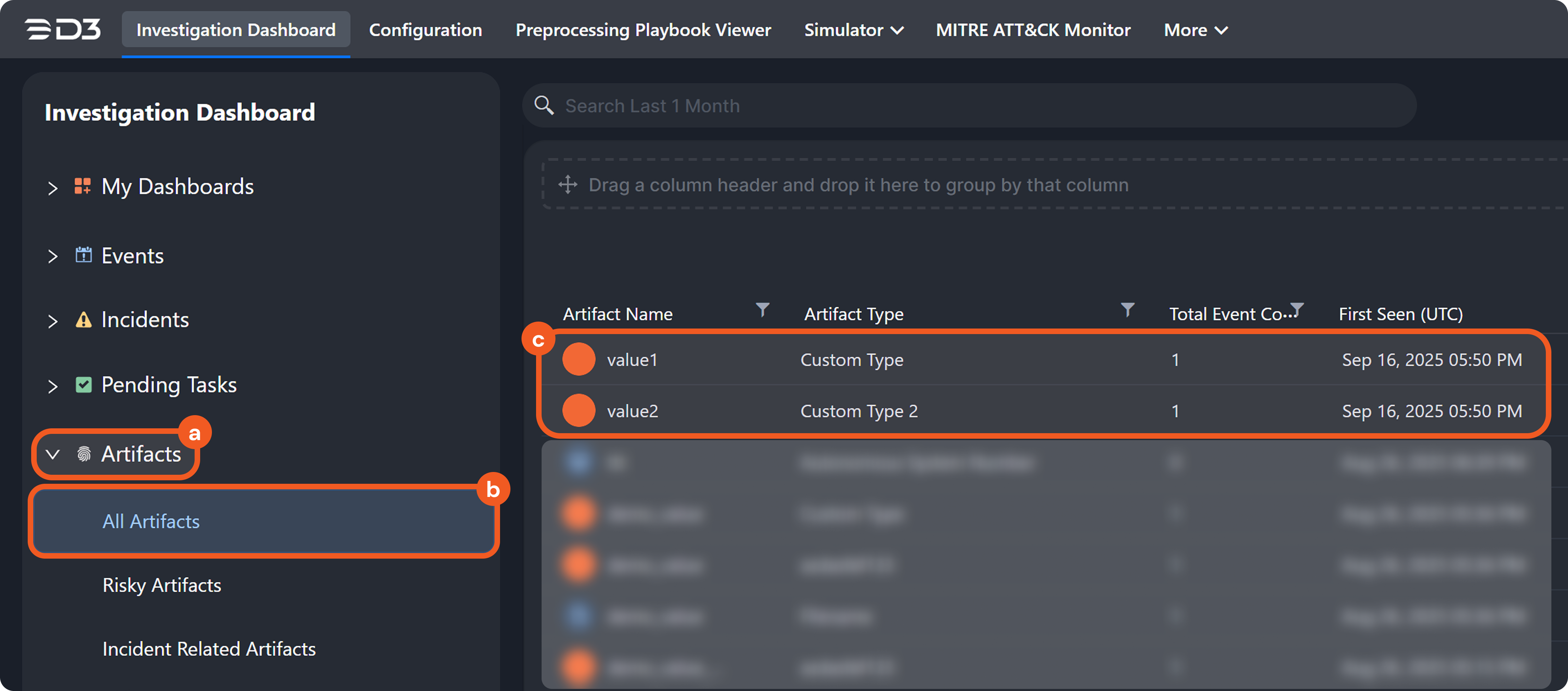
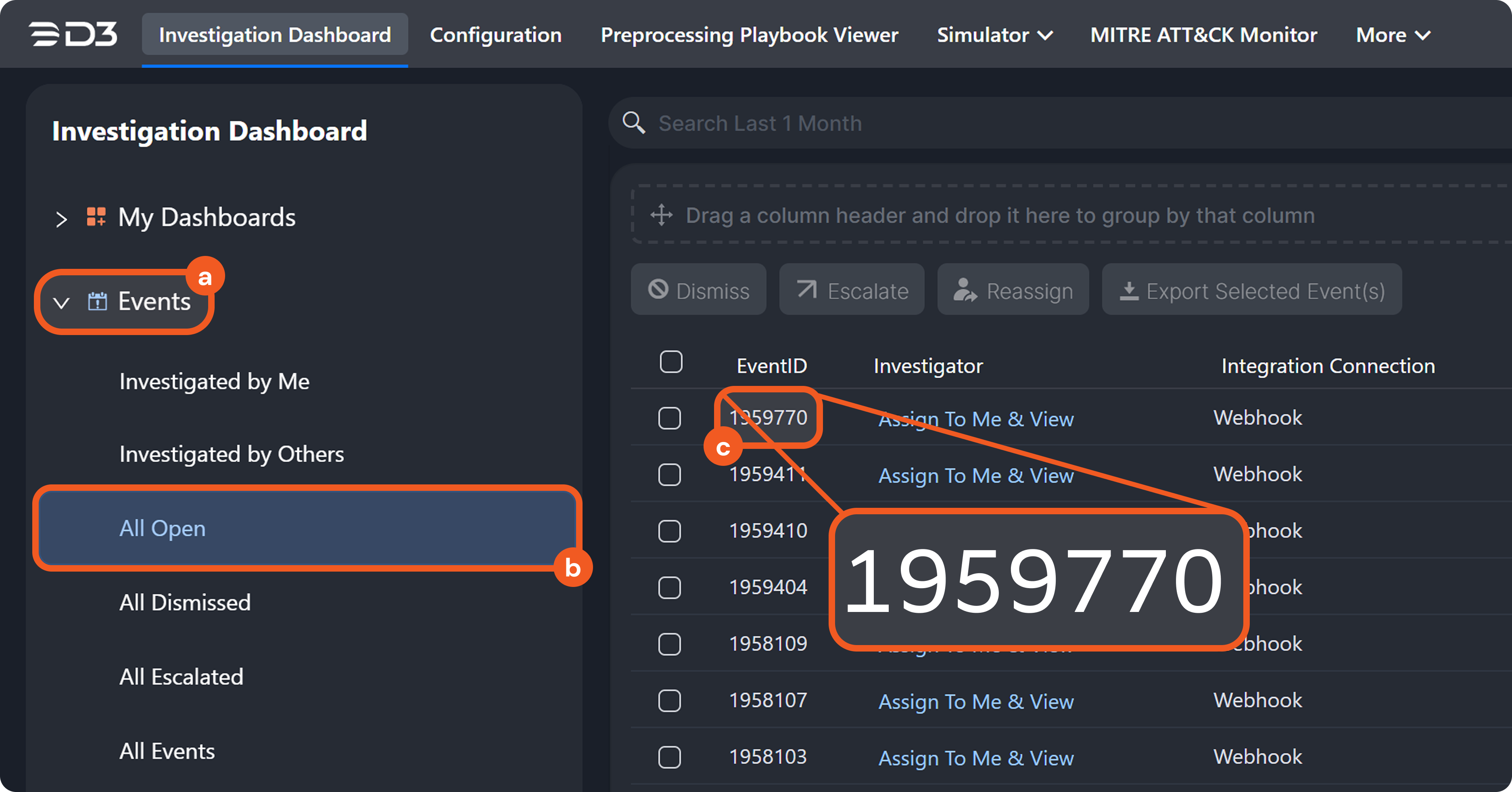
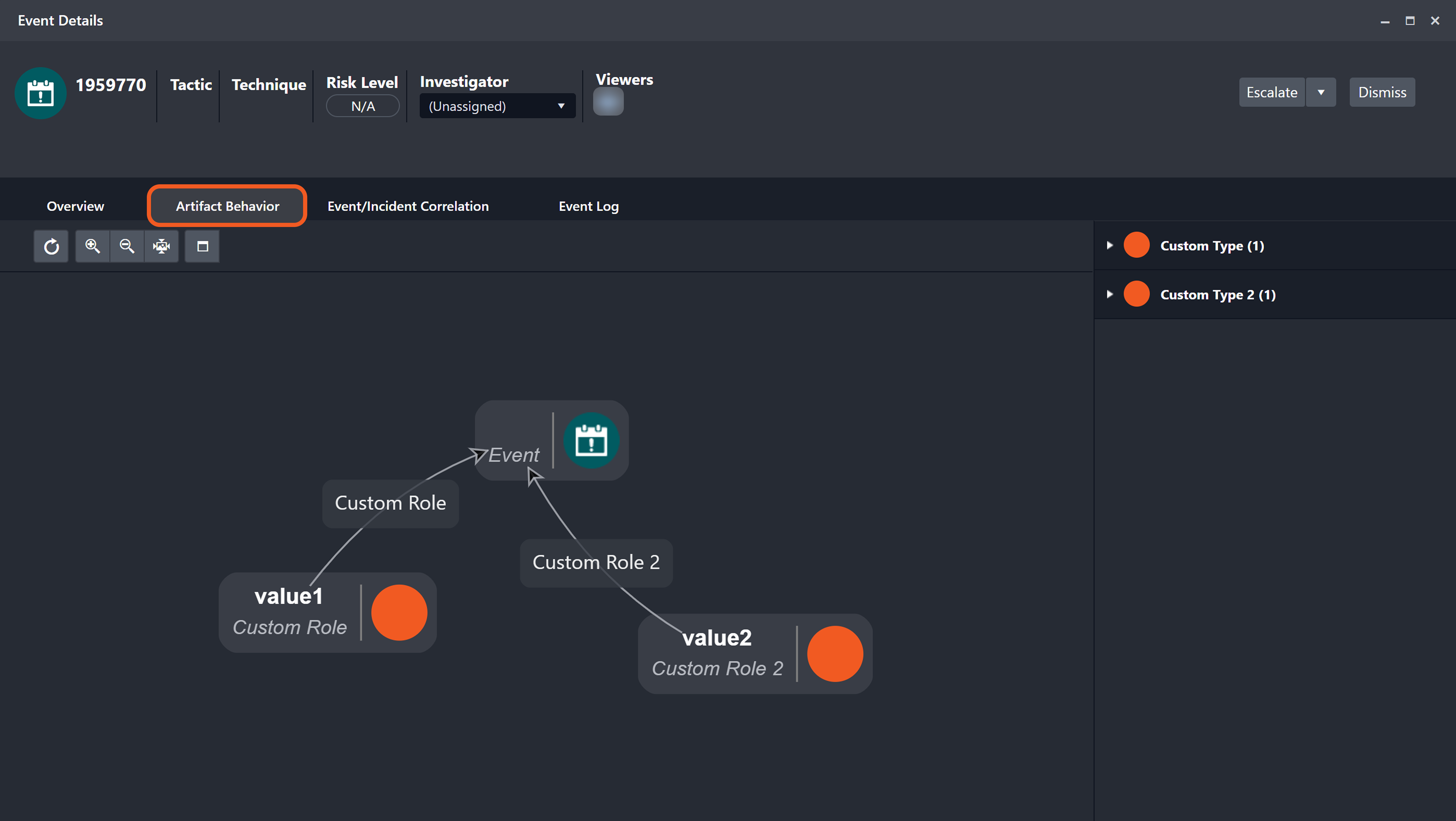
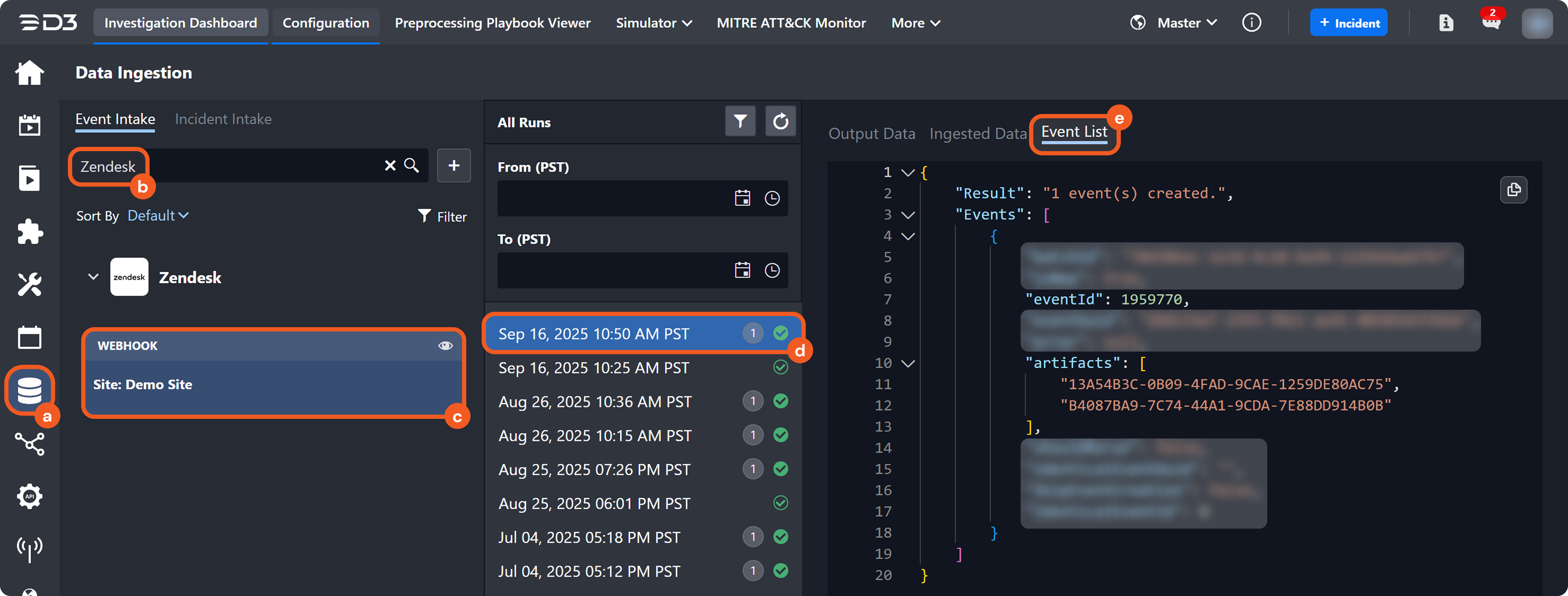
Artifact instances and their relationships together form a behavior graph. This graph is displayed in the Artifact Behavior tab of a D3 event's Event Details popover.
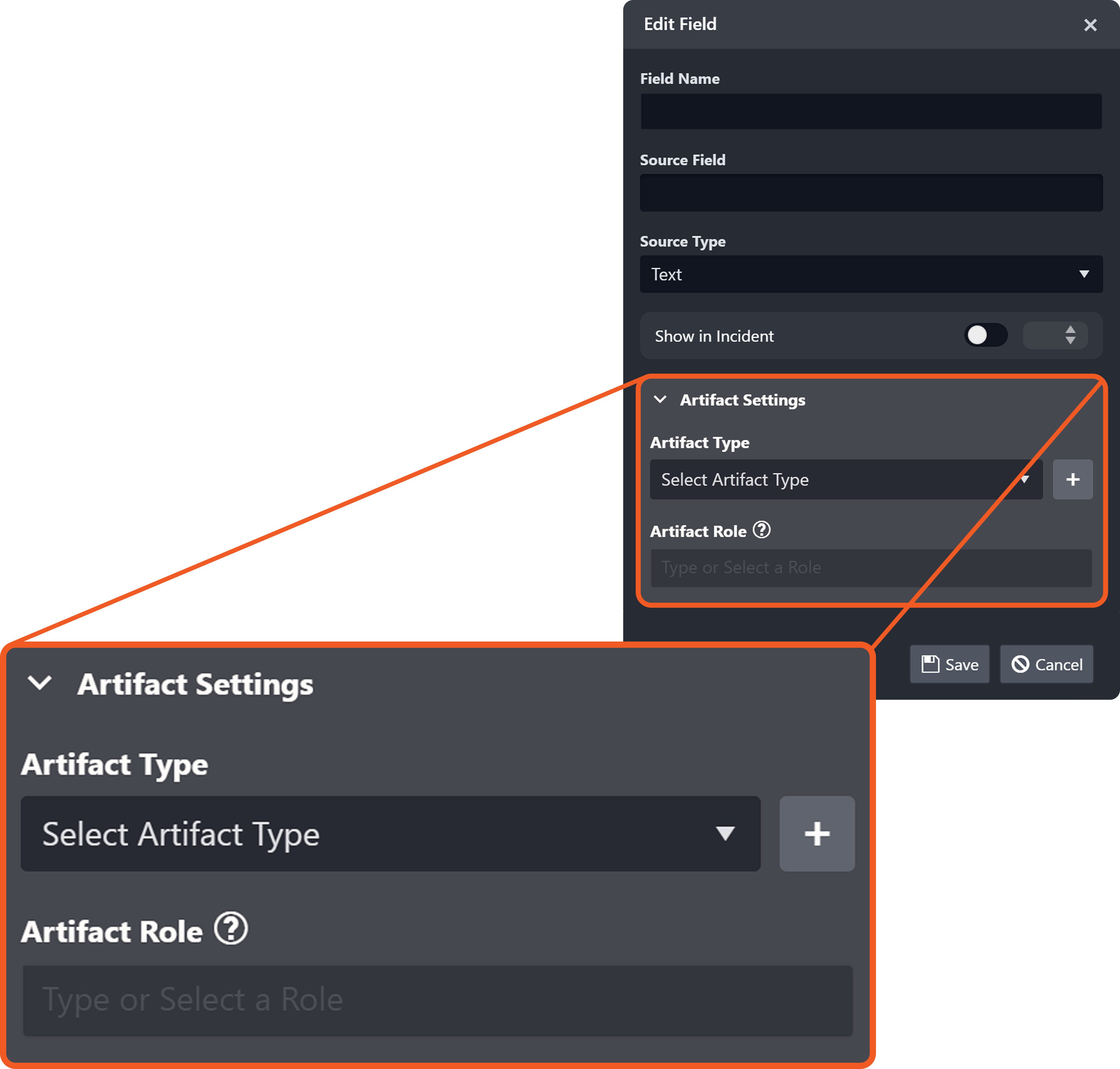
Artifact Settings
Configurable Parameters
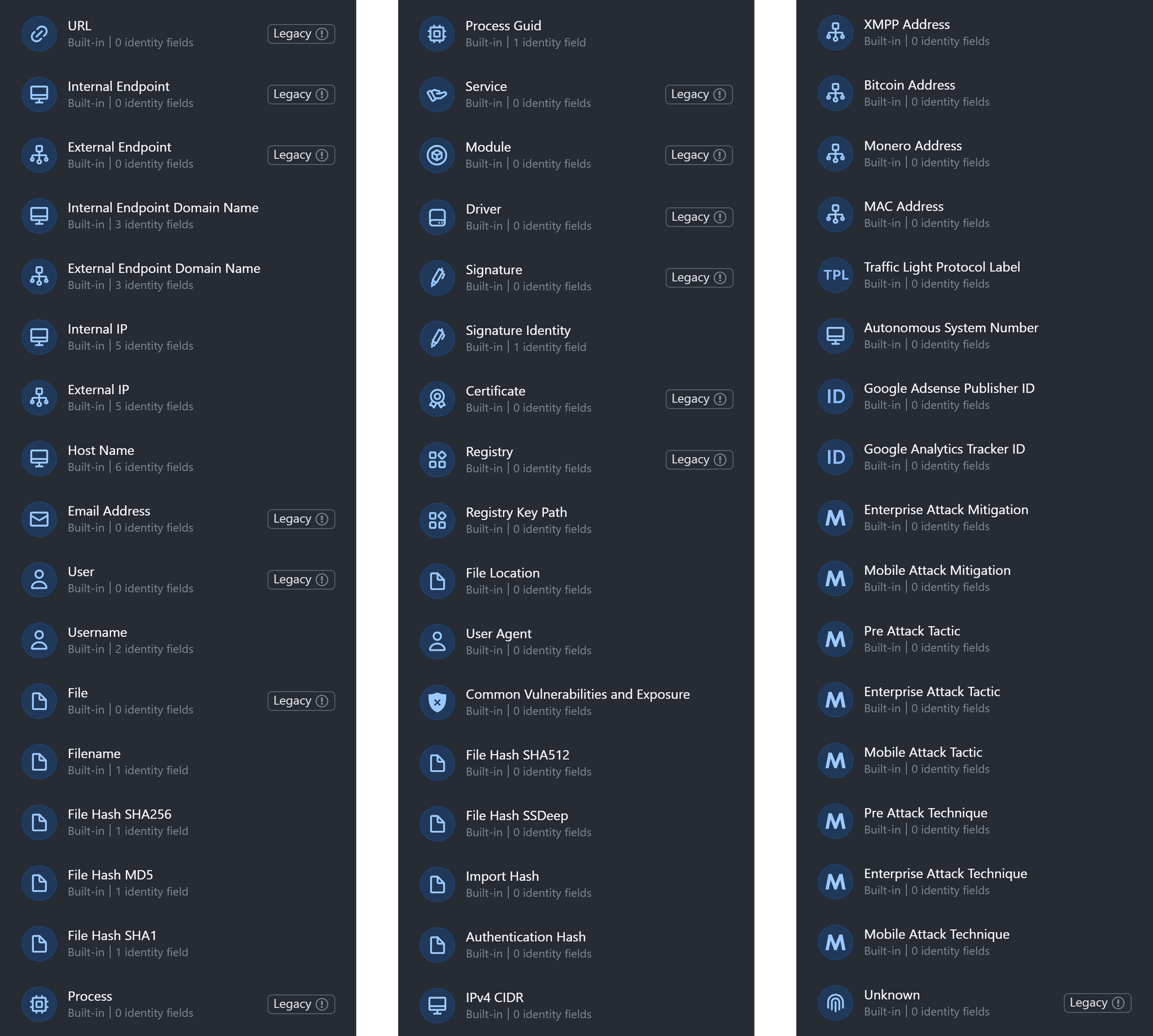
Artifact Role: A label that clarifies the function of an artifact in relation to an event.
Each string entered and saved in this field becomes a selectable option in the Relationship popover for the chosen artifact type, within the Artifact module.
By default, the value of the artifact role is identical to the artifact type.
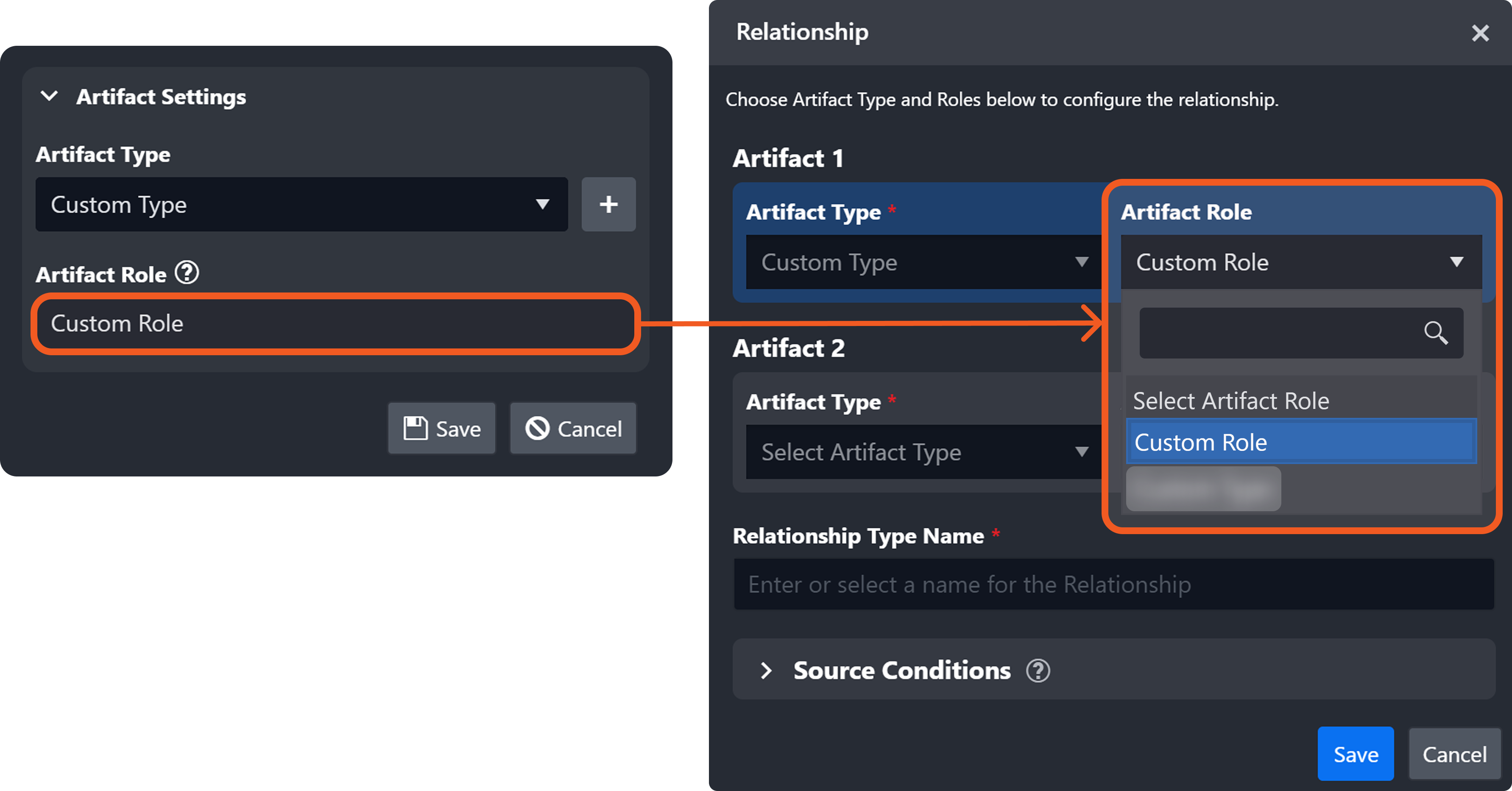
Defining and Using Artifact Roles
Understanding Artifact Instantiation
An artifact is instantiated after data ingestion, when the following conditions are met:
The configured source field value for an EFM record matches a key in the raw data JSON.
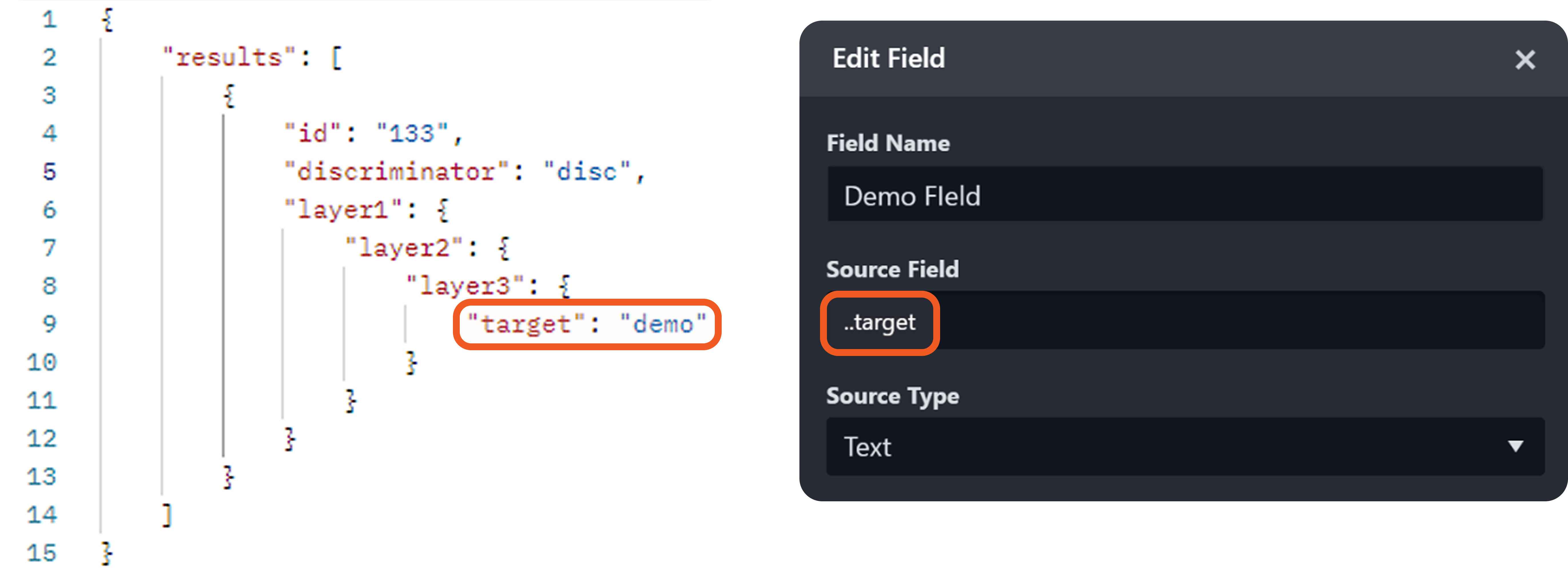
The value of the matched key is not:
an empty string
an empty list
null
An artifact type for the EFM record is configured.
%201-20250624-003750.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250630-175639.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250630-183146.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250630-185035.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250718-190151.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250718-190210.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250916-172631.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250630-190451.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)
-20250630-190521.png?inst-v=a955d7a2-4130-4c65-a33e-27e848ba2a1c)